test for ligament tear|test for knee ligament injury : advice Valgus stress test for Medial Collateral Ligament It is performed with the patient supine and the knee in 20° of flexion. With one hand on the lateral aspect of the knee and the other on the foot, the examiner gently abducts and externally rotates the lower leg. Increased . See more The only effective method for sterilizing media is to use an autoclave or a laboratory pressure cooker. Sterilization can only be guaranteed when the parameters of 121°C for 15 to 30 .
{plog:ftitle_list}
How often does the CDC require that autoclaves be tested to ensure they are properly sterilizing implements?Hazardous materials include explosives, flammable and combustible substances, poisons, and radioactive materials. Many products containing hazardous chemicals are routinely used and stored in homes. These materials can cause death, serious injury, long-lasting health effects, .
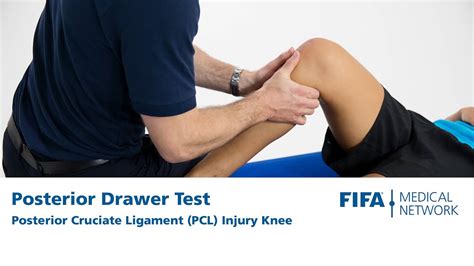
Lacchman’s test It is performed with the patient supine and the knee flexed 20–30°. The examiner grasps the distal femur (from lateral side) with one hand and the proximal tibia with the other hand (from medial side). The lower leg is given a brisk forward tug in an attempt to identify a discrete endpoint. A . See morePosterior Drawer Test This test is performed with the patient supine and the knee flexed to 90°. There are two different ways it may be . See moreMcMurray Test The McMurray test is performed with the patient supine and the examiner grasping the medial aspect of the affected knee with one hand and the patient’s heel with . See more
Valgus stress test for Medial Collateral Ligament It is performed with the patient supine and the knee in 20° of flexion. With one hand on the lateral aspect of the knee and the other on the foot, the examiner gently abducts and externally rotates the lower leg. Increased . See more An MRI can show the extent of an ACL injury and signs of damage to other tissues in the knee, including the cartilage. Ultrasound. Using sound waves to visualize internal . The Lachman test is the test of choice for the acutely injured knee. The reasons for this are: An acute injury with an associated haemarthrosis prevents knee flexion to 90 degrees. Protective spasm of the hamstring muscles is negated with the joint extended. An MRI can show the extent of an ACL injury and signs of damage to other tissues in the knee, including the cartilage. Ultrasound. Using sound waves to visualize internal structures, ultrasound may be used to check for injuries in the ligaments, tendons and muscles of .
The Lachman test is a specific clinical exam technique used to evaluate patients with a suspected anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury. The test relies on proper positioning and technique and is regarded as the most sensitive and specific test .
test for knee ligament injury
The Lachman test is used to diagnose ACL injuries. It's considered very accurate and can help guide treatment to get your knee back to its normal range of motion.The Lachman test is a passive accessory movement test of the knee performed to identify the integrity of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). The test is designed to assess single and sagittal plane instability. Knee Ligaments including ACL. ACL from Above. Technique. Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with presence of a traumatic knee effusion with increased laxity on Lachman's test but requires MRI studies to confirm diagnosis. Treatment involves ligamentous reconstruction utilizing a variety of techniques and graft choices depending patient age and activity levels. Epidemiology. Incidence. common. X-ray: A torn ligament will not show up on an X-ray, but an X-ray can find fractured or broken bones that might occur separately or alongside a ligament injury. MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be done to see if there is a partial or complete ligament tear.
A positive Lachman test or pivot test is strong evidence of an existing anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear, and a negative Lachman test is fairly good evidence against that injury..
lachman's test positive
X-ray. This imaging test can rule out an injury to bone instead of a ligament injury. It uses energy beams to make images of internal tissues, bones, and organs on film. MRI. This test uses large magnets, radio waves, and a computer to make detailed images of . An anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear is a knee joint injury that usually occurs while playing sports. It causes leg pain and instability of the knee. This is one of the most common injuries among recreational athletes of all ages. A physical examination diagnoses an ACL tear.
The Lachman test is the test of choice for the acutely injured knee. The reasons for this are: An acute injury with an associated haemarthrosis prevents knee flexion to 90 degrees. Protective spasm of the hamstring muscles is negated with the joint extended.
An MRI can show the extent of an ACL injury and signs of damage to other tissues in the knee, including the cartilage. Ultrasound. Using sound waves to visualize internal structures, ultrasound may be used to check for injuries in the ligaments, tendons and muscles of . The Lachman test is a specific clinical exam technique used to evaluate patients with a suspected anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury. The test relies on proper positioning and technique and is regarded as the most sensitive and specific test .
The Lachman test is used to diagnose ACL injuries. It's considered very accurate and can help guide treatment to get your knee back to its normal range of motion.The Lachman test is a passive accessory movement test of the knee performed to identify the integrity of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). The test is designed to assess single and sagittal plane instability. Knee Ligaments including ACL. ACL from Above. Technique. Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with presence of a traumatic knee effusion with increased laxity on Lachman's test but requires MRI studies to confirm diagnosis. Treatment involves ligamentous reconstruction utilizing a variety of techniques and graft choices depending patient age and activity levels. Epidemiology. Incidence. common.
abcam p24 elisa kit
X-ray: A torn ligament will not show up on an X-ray, but an X-ray can find fractured or broken bones that might occur separately or alongside a ligament injury. MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be done to see if there is a partial or complete ligament tear. A positive Lachman test or pivot test is strong evidence of an existing anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear, and a negative Lachman test is fairly good evidence against that injury..
X-ray. This imaging test can rule out an injury to bone instead of a ligament injury. It uses energy beams to make images of internal tissues, bones, and organs on film. MRI. This test uses large magnets, radio waves, and a computer to make detailed images of .
abcam pge2 elisa kit
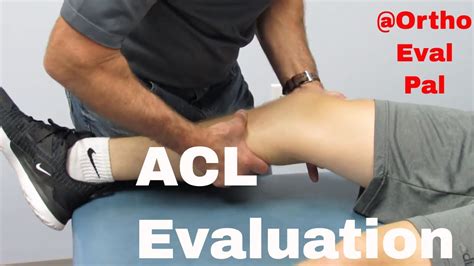
lachman test vs anterior drawer
Hydrothermal laboratory reactor available with a pressure gauge to maintain appropriate pressure condition required for the chemical reaction. It also comes with features of self-heating with all .25x Shown with Optinal Base, CAUTION! READ THESE IMPORTANT SAFEGUARDS! .
test for ligament tear|test for knee ligament injury